OGURA FABRIC
JAPANESE SILK jacquard FACTORY
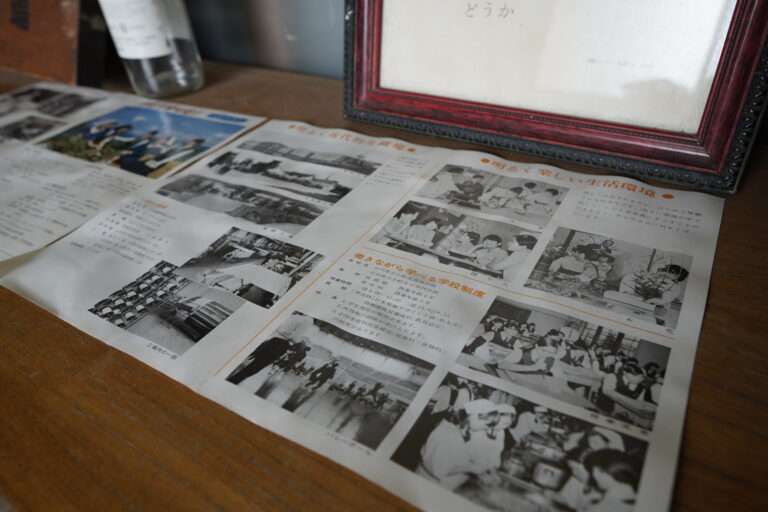
Established in 1895, the company specializes in Japanese silk Jacquard and has over 100 years of tradition and history. Before the war, the company’s main products were the “Mon-Habutae”. After the war, it was one of the first to produce wide-width patterned fabrics for export and the domestic market. In 1951, when the US Silk Industry Delegation visited Japan, Wolter Strassberger, President of the American Silk Industry Association, came to the company through the arrangement of the Nozawa-gumi trading company. The company has also received visits from the Imperial Family on numerous occasions.
小倉織物は、1895年創業、100年以上の伝統と歴史を持つ日本製シルクジャガード専門メーカーです。戦前の同社の主力商品は「紋羽二重」でした。戦後、輸出および国内市場向けに広幅の柄生地をいち早く生産した会社の1つです。1951年に米国絹産業代表団が来日した際、野沢組の計らいで米国絹産業協会会長ウォルター・ストラスバーガー氏が来社しました。また日本の皇室の御来臨を何度も受けています。





糊付けと乾燥 :生糸は「綛(かせ)」の状態でケースに入って工場に入荷した後、そこから綛を取り出してお湯を張り、綛の生糸を漬込みます。そこに糊材を入れて一両日漬け込み寝かします。次に昭和20年代製造の脱水機に掛けて綛を絞ります。そして綛を物干し竿に掛けてボイラーを焚き強制乾燥を行います。この後更に天日乾燥を行って準備は完成です。
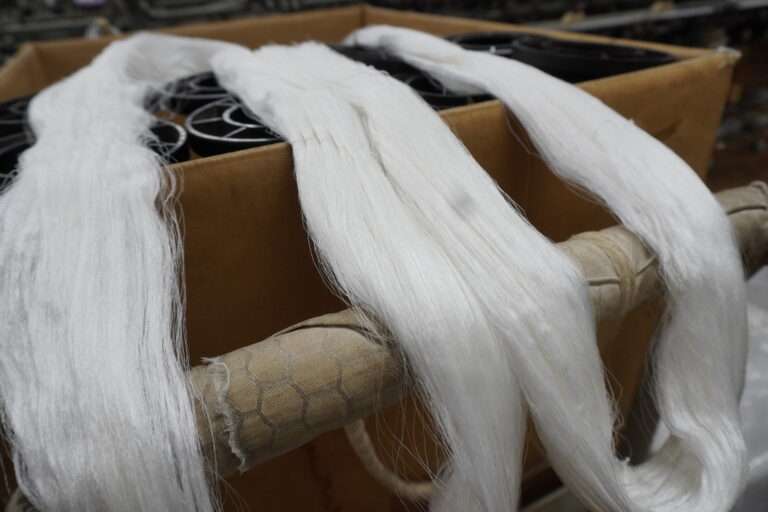
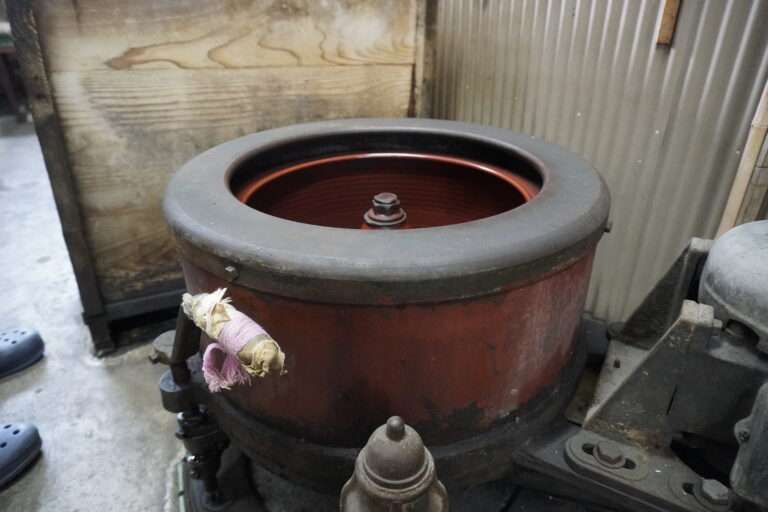
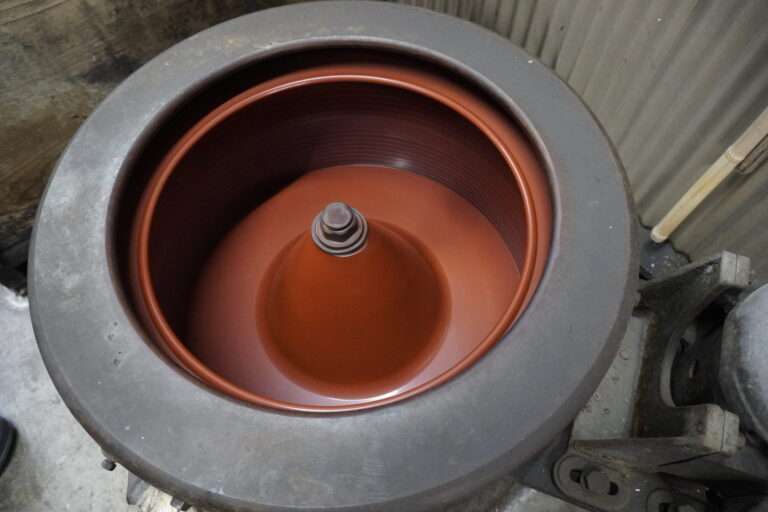
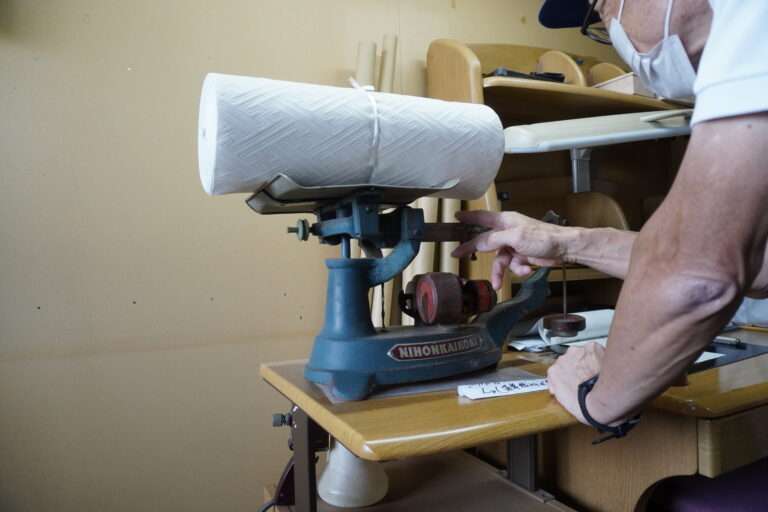
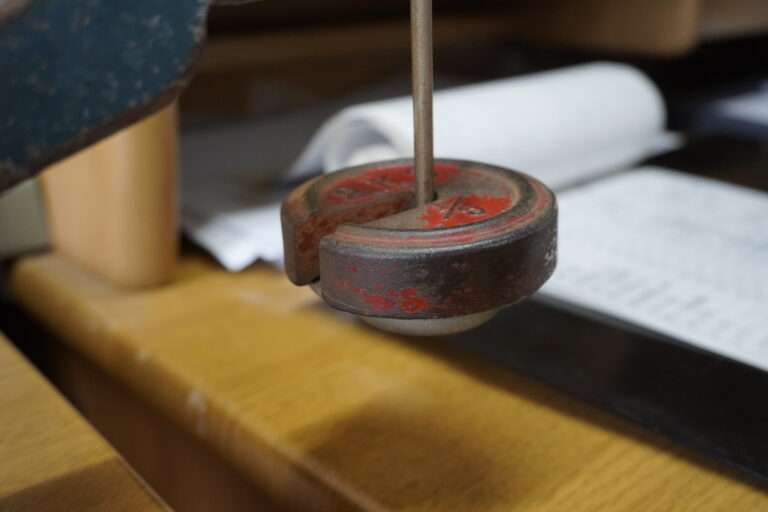
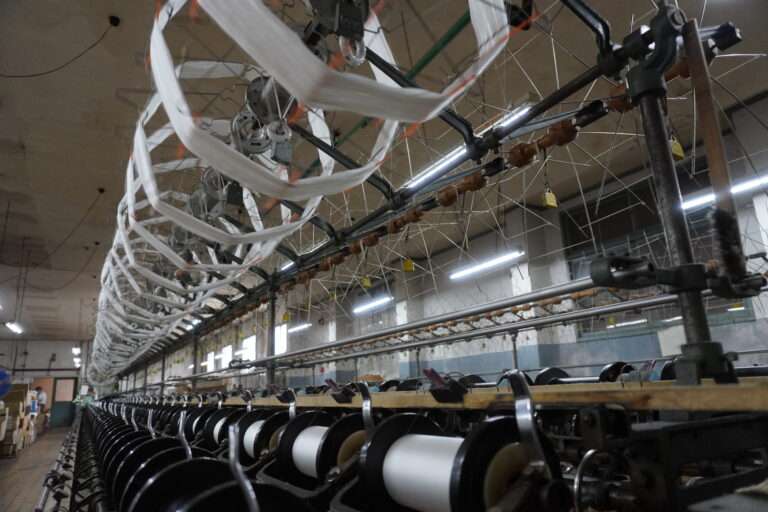
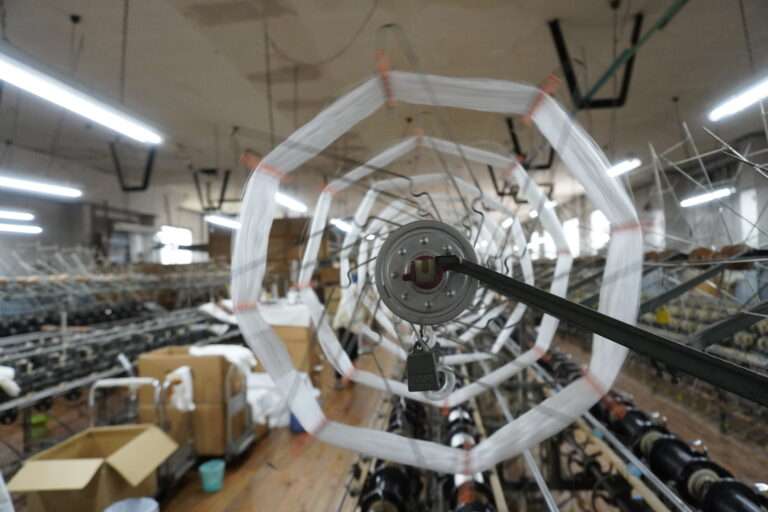
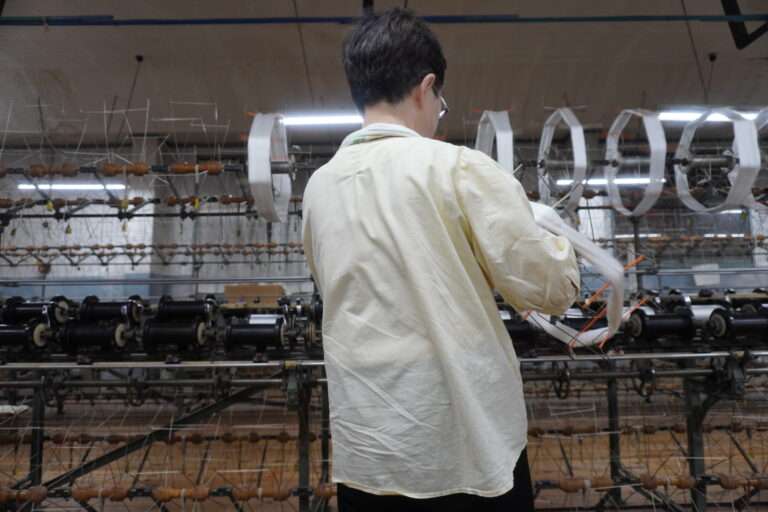
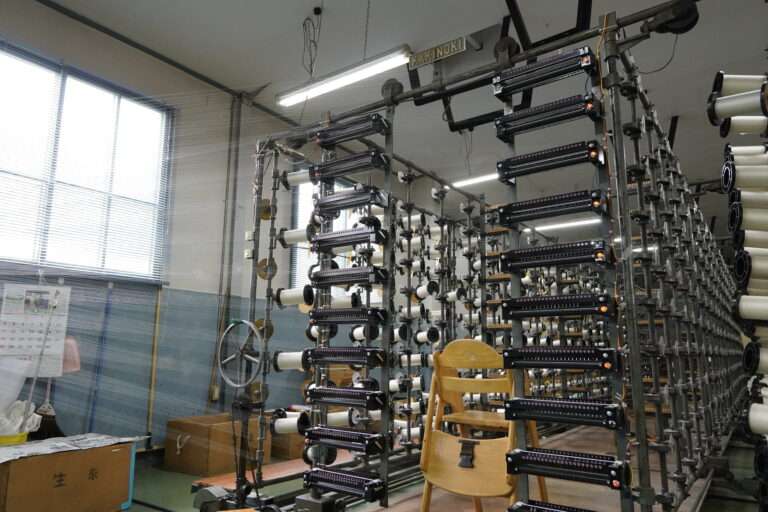
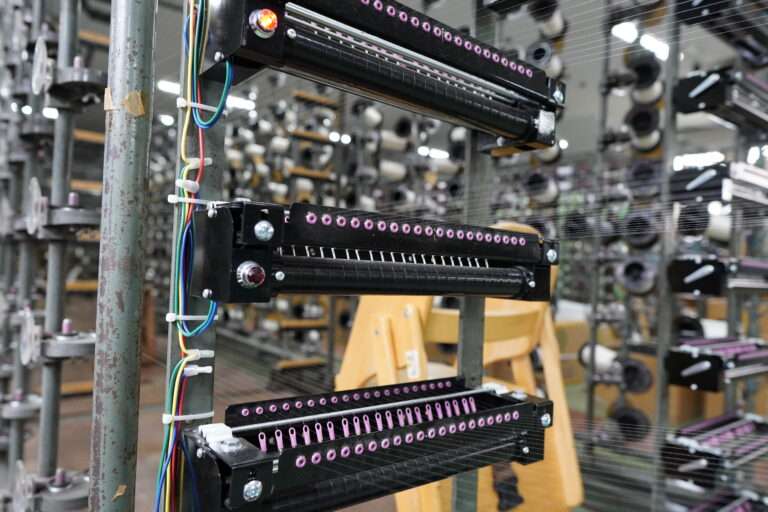
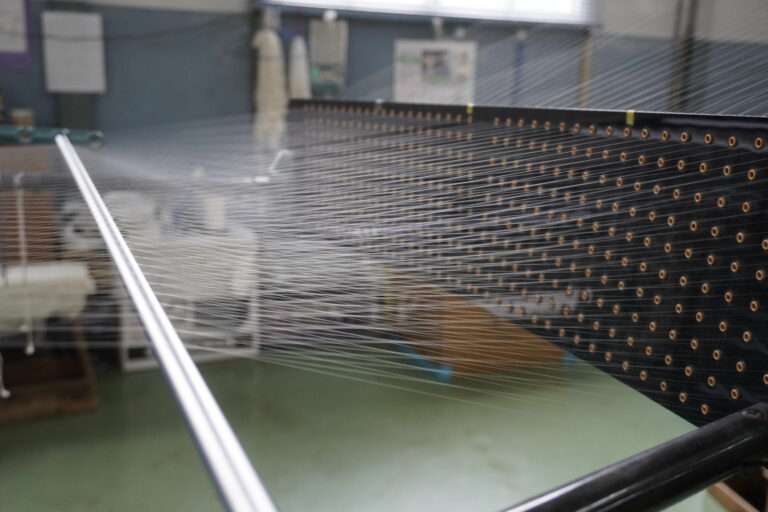
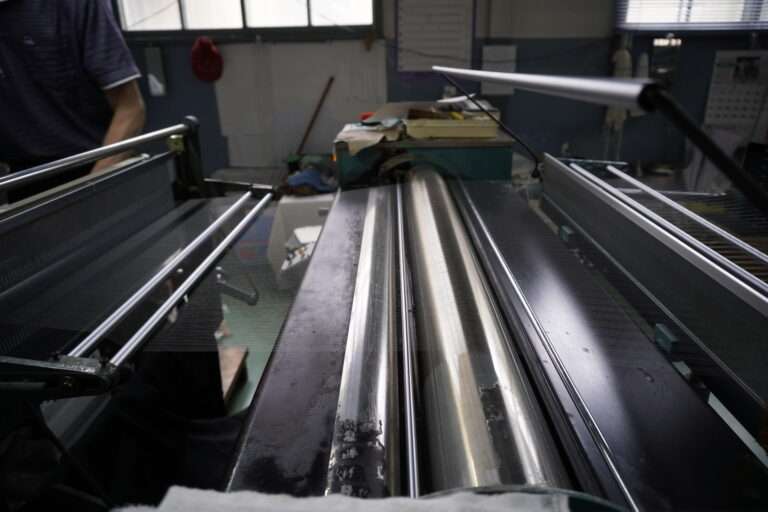
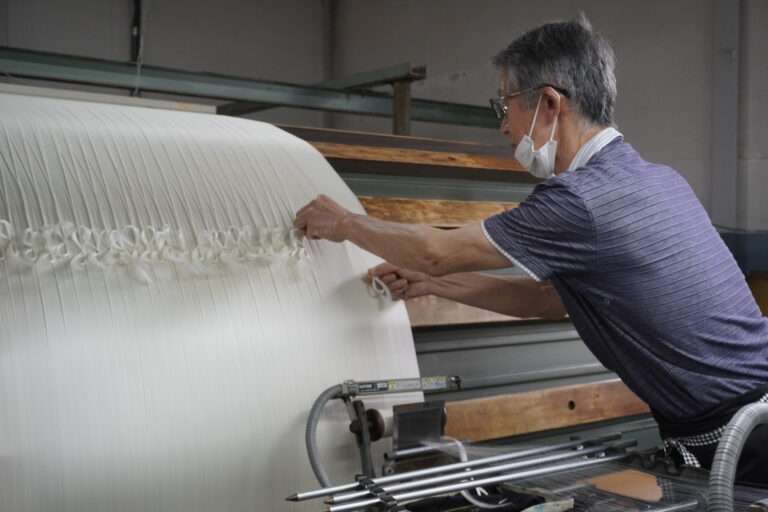



















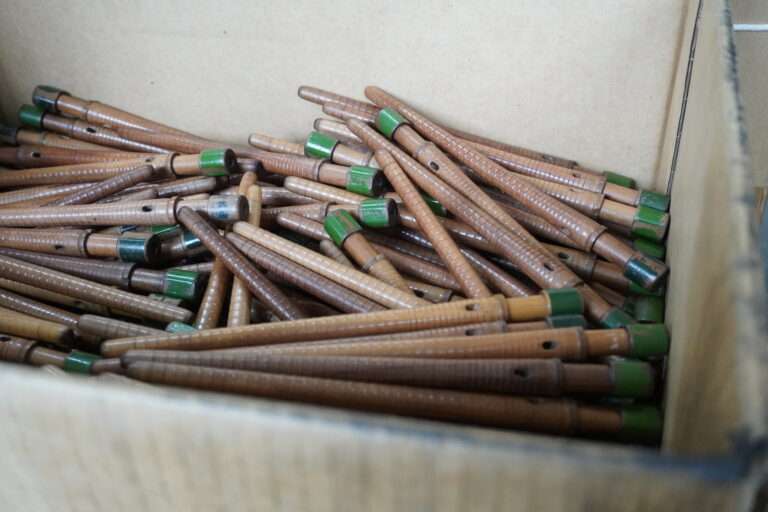
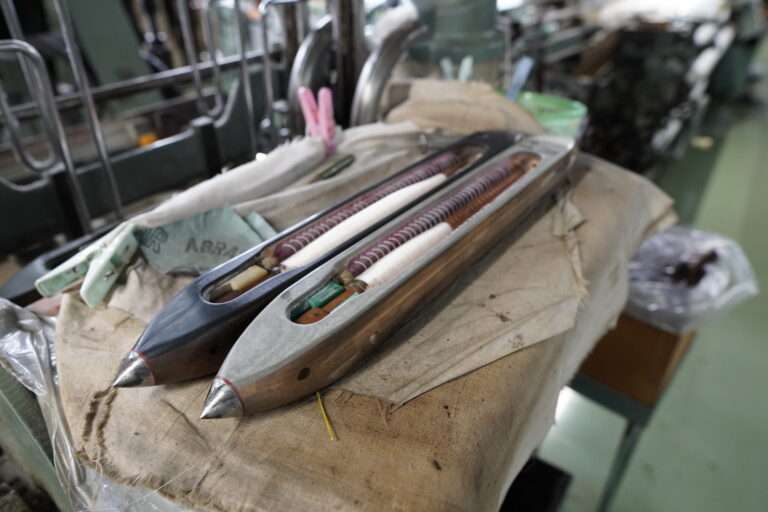
管巻き : シャトルに入れるための緯糸を木管に巻きます。このシャトル用の木管は個別と複数で巻く機械があります。巻かれた木管は終了と同時に自動的に入れ替え作業を行えます(動画参照)。
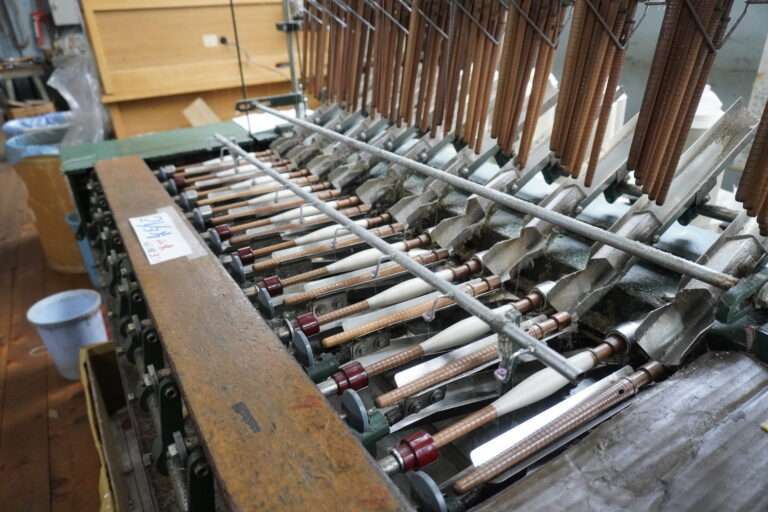
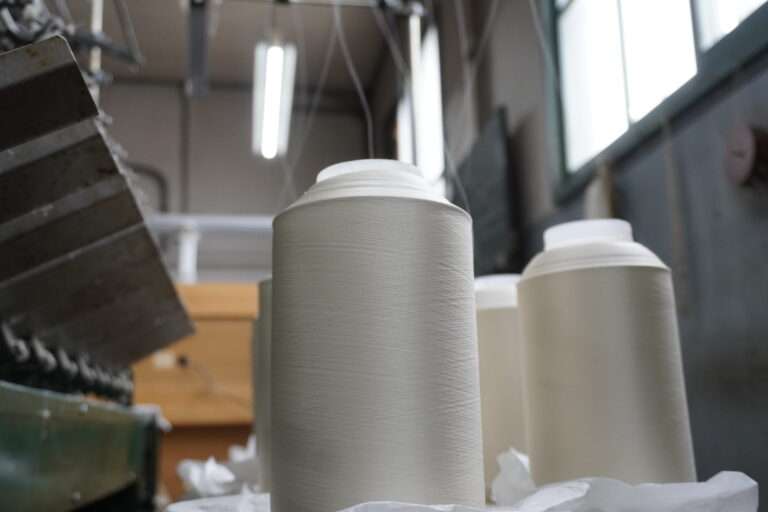



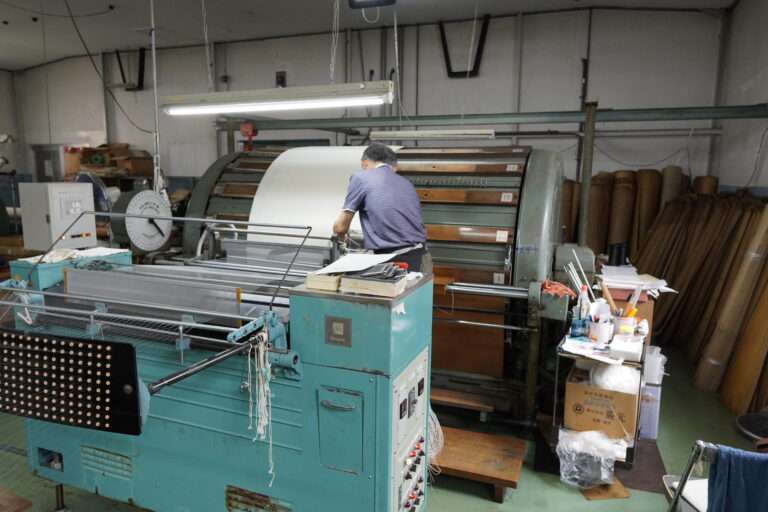
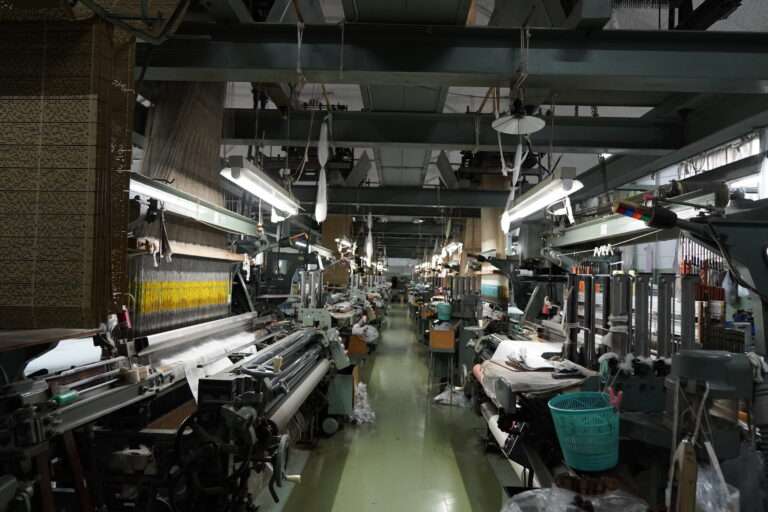
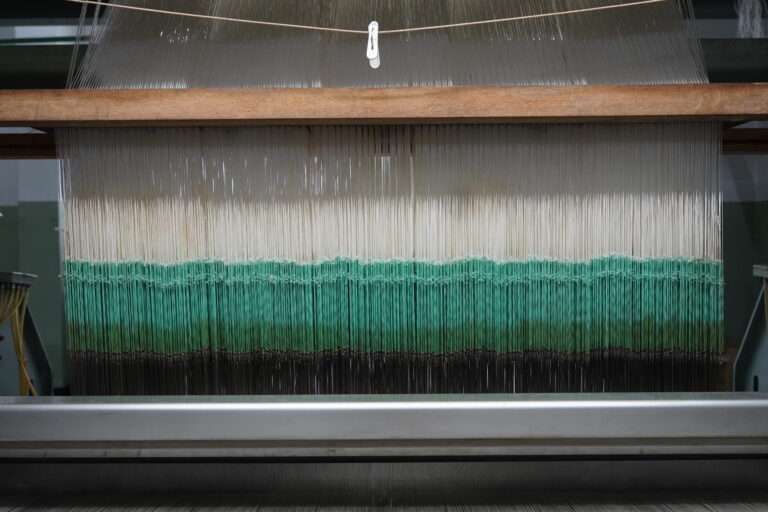
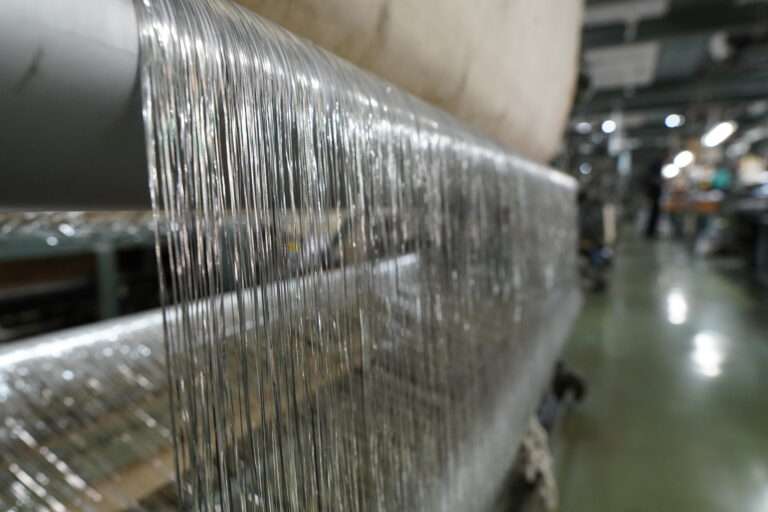
整織 : ジャカード織は、柄そのものを生地に織り込む織物のこと。小倉織物は複数台のジャガード織機を用意していいます。生地の上に柄をプリントするプリント生地とは異なり、生地に直接柄が織り込まれているため、高級感や自然な立体感があり、糸の種類を組み合わせることで幅広いデザインが楽しめます。








Jacquard built upon the work of earlier inventors. Basile Bouchon, in 1725, developed an attachment for draw looms that used a strip of punched paper to select the raised warp threads during weaving. However, Bouchon’s loom had limitations in handling a significant number of warp threads. Jean Falcon, a master silk weaver, improved upon Bouchon’s mechanism in 1737 by replacing the paper strip with a chain of punched cards, allowing for the deflection of multiple rows of hooks simultaneously.
Jacques de Vaucanson, known for his mechanical toys, attempted to automate Bouchon’s mechanism between 1747 and 1750. Vaucanson’s mechanism used long pins or “needles” pressed against a punched paper sheet wrapped around a perforated cylinder to select the hooks that lifted the warp threads. However, his loom, like Bouchon’s, couldn’t control enough warp threads for elaborate patterns.
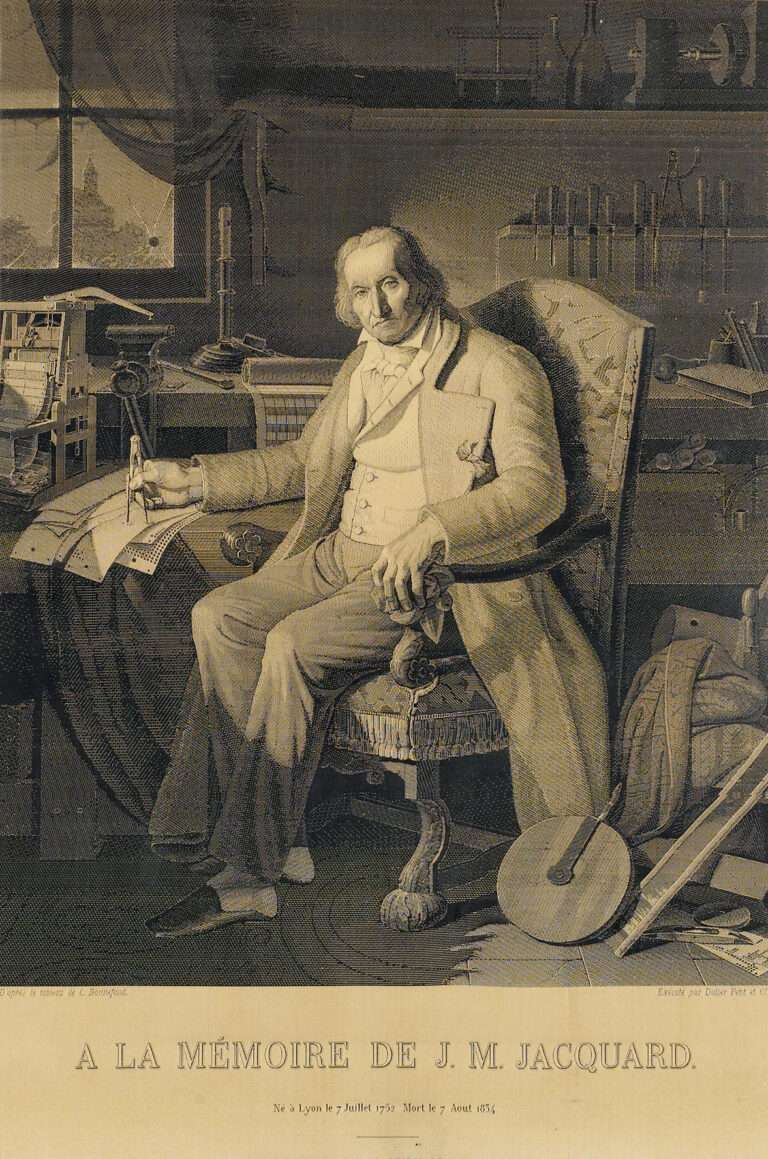
In 1804, Jacquard examined Vaucanson’s loom stored at the Conservatoire des Arts et Métiers in Paris. Inspired by Falcon’s chain of punched cards, Jacquard eliminated the paper strip and reintroduced the card system. Recognizing the potential of Jacquard’s loom, Emperor Napoleon and Empress Josephine visited Lyon on April 12, 1805, to witness its capabilities. On April 15, 1805, Emperor Napoleon granted Lyon the patent for Jacquard’s loom, while Jacquard himself received a lifelong pension and royalties for each loom sold and used between 1805 and 1811.
This innovation by Jacquard played a significant role in stimulating the French textile industry, which was competing with Britain’s industrialized industry. The Jacquard loom revolutionized weaving, allowing for the production of intricate and highly patterned fabrics with increased efficiency and accuracy. To comprehend the Jacquard loom, it is helpful to have a basic understanding of weaving. The loom consists of a rectangular frame where parallel threads, known as the warp, are stretched. In the case of plain cloth, every other warp thread is raised. A weft thread, positioned at a right angle to the warp, is then passed through the space called the “shed” between the lower and upper warp threads. Subsequently, the raised warp threads are lowered, the alternate warp threads are raised, and the weft thread is passed through the shed in the opposite direction. Through numerous repetitions of this process, the fabric gradually takes shape.
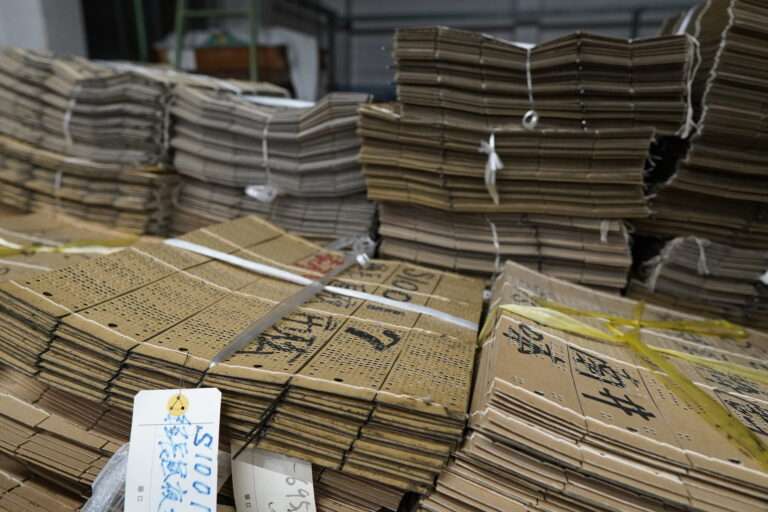
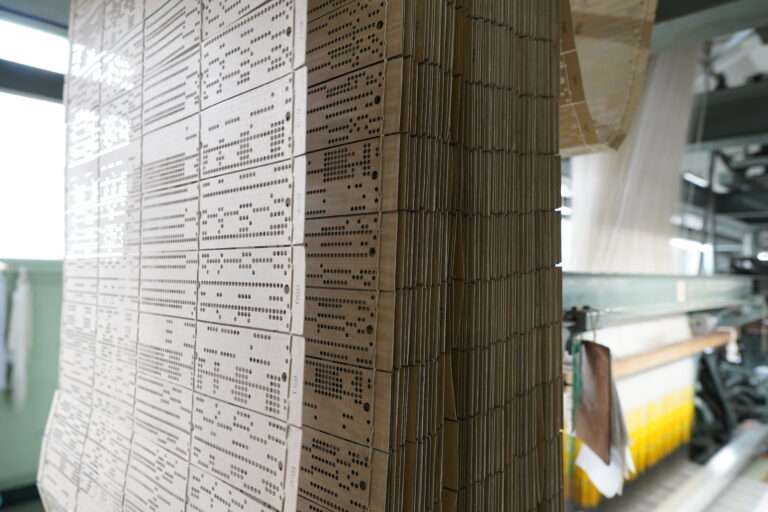
▪️ Card Design: The desired pattern is translated into a series of holes or perforations on a series of punched cards or a punched paper roll. Each row of holes represents one row of the fabric’s design.
▪️ Card Reading: The punched cards or paper roll are placed in sequence on a rotating cylinder or drum. As the loom operates, the Jacquard machine reads the pattern from the cards or paper roll one row at a time.
▪️ Loom Control: The Jacquard machine uses the information from the punched cards or paper roll to control the individual warp yarns. It lifts or lowers the specific warp threads corresponding to the pattern, allowing the weft (crosswise) yarns to pass through and create the desired design.
▪️ Shedding: The Jacquard machine controls the shedding mechanism, which creates an opening or shed between the warp yarns to allow the weft yarn to be inserted during the weaving process.
▪️ Weft Insertion: The weft yarn is inserted into the shed created by the shedding mechanism, passing through the open warp threads according to the pattern specified by the Jacquard machine.
▪️ Beat-up: After the weft yarn is inserted, the Jacquard machine releases the tension on the warp threads, and the beat-up mechanism pushes the woven weft yarn into place.
▪️ Repeat: The process is repeated for each row of the fabric’s design, with the Jacquard machine reading the pattern from the punched cards or paper roll and controlling the warp yarns accordingly.
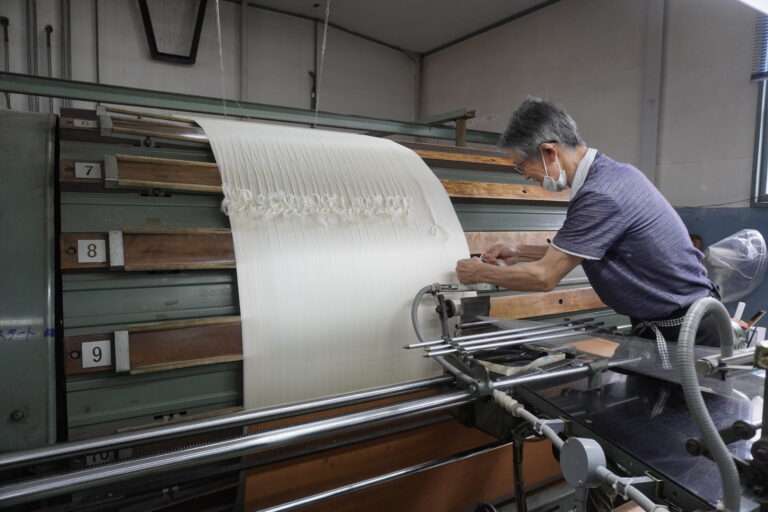
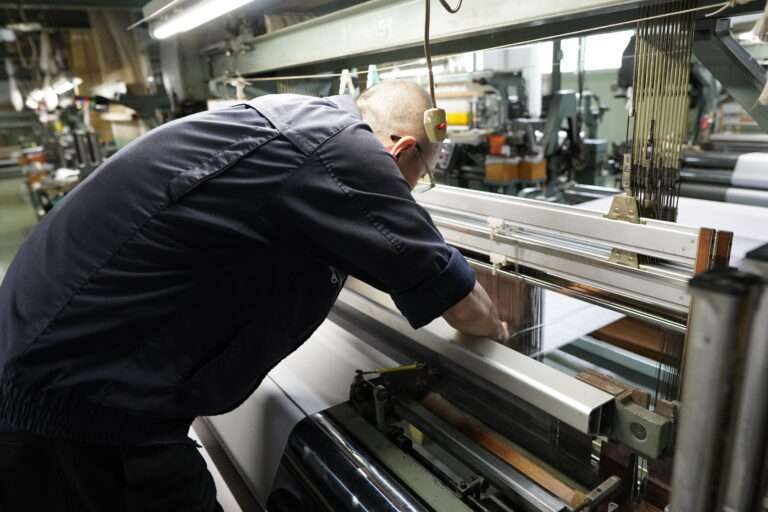
検反作業 : シルクの織物は大変繊細な生地です。各繊維を綿密に検査する必要があります。これには経験豊富な目が必要です。一つ一つ虫眼鏡で確認する作業は、細やかな作業が必要です。ベテランの作業員が丁寧に確認していきます。
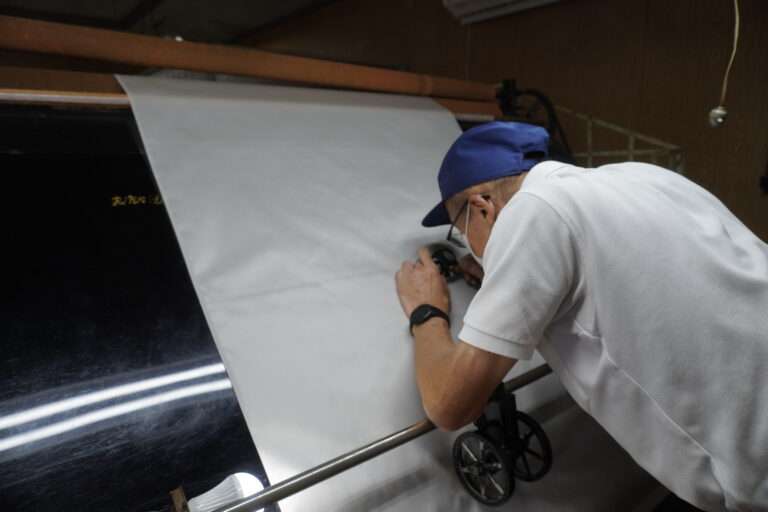
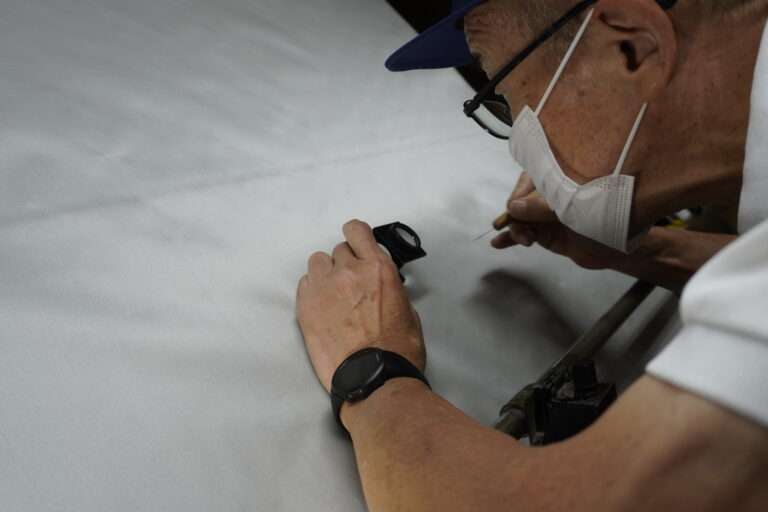
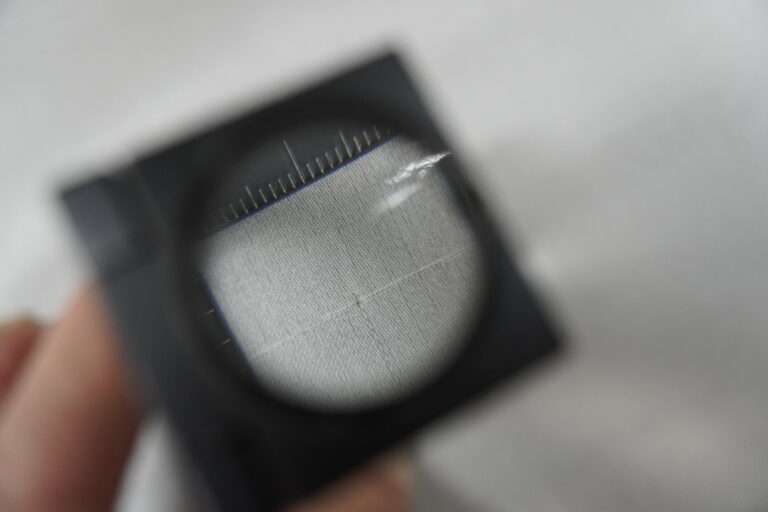




この後に最終検反が終わり精練加工場に出荷します。

We are the Silk jacquard specialized company of Japan with the tradition and history for over a hundred years.
Figured habutae and the Komatsu figured satin were the main force of production at prewar days, and after the war, the Couhabamon cloth was produced for exporting and domestic use. In 1951, with the arrangement of Nosawa Co., Ltd., Mr. Walter Strasburger, chief director of the United States Silk trade association visited our company during the United States Silk trad missionary. Also in 1953, the present emperor had sent it as a gift for the coronation of Queen Elizabeth of Great Britain during his Prince age. Currently, our business development advances not only to Silk but to synthetic fiber and in the field of chemical fibers.
明治28年創業。100年有余の伝統と歴史を誇る日本のシルクジャガードの専門企業。
戦前は、紋羽二重、小松綸子を生産の主力とし、戦後は、いち早く広巾紋織物を輸出および国内向けに生産する。昭和26年には、米国絹業使節団の来日に際し、貿易商野澤組の計らいでウオルターストラスバーガー米国絹業協会理事長が来社。また、皇室のご来駕も幾度となく賜っております。
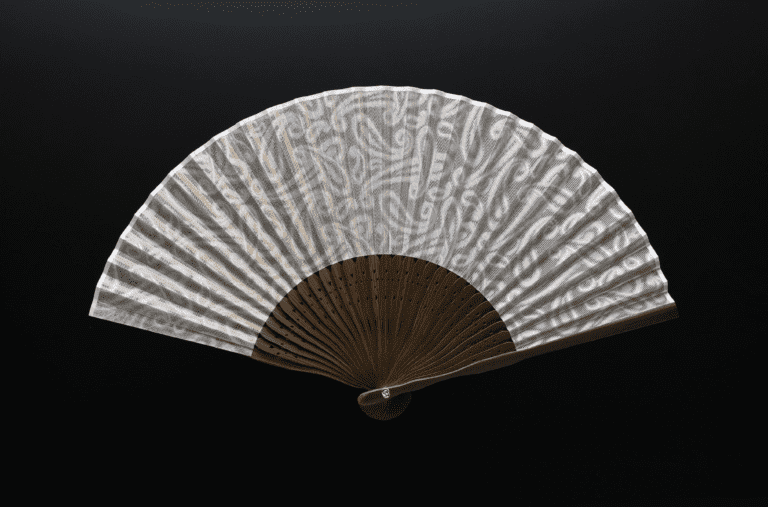
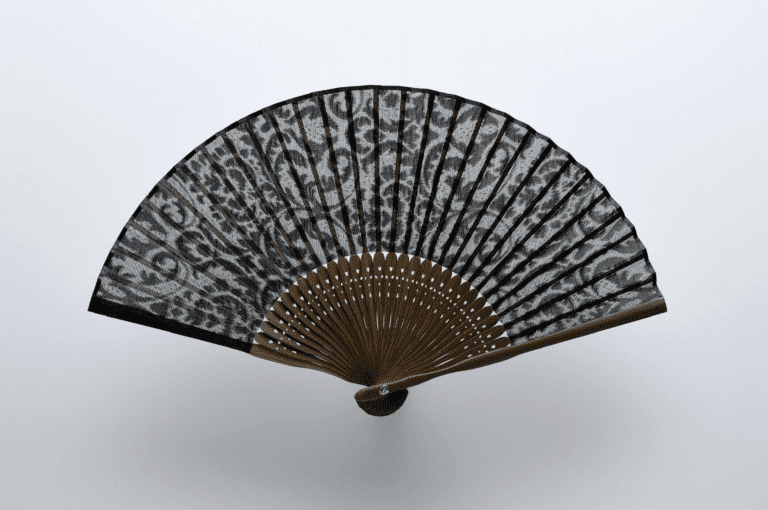




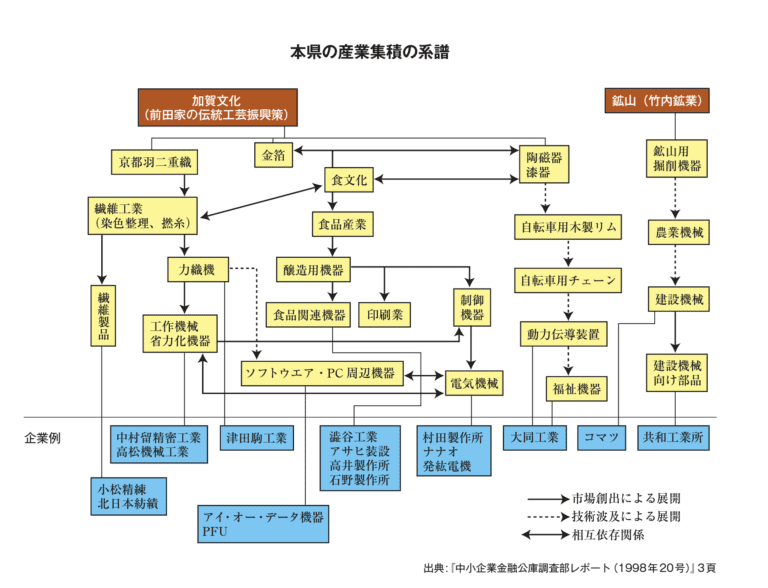
加賀藩の文化政策(明治元年以前)は、芸能や工芸、さらには食文化に至るまで洗練されたものになりました。特に技術面で特筆すべきは御細工所の存在でした。御細工所は藩営の工芸工場であったが、当初は武具が中心であったものが、特に三代藩主前田利常の時代には、蒔絵、象嵌、和紙、竹細工など幅広い工芸品を扱うようになりました。 加賀藩の藩主御用達の家具を作る職人たちは、地元の職人を雇うだけでなく、全国から学問や芸能、工芸に携わる人材を登用し、文化の広がりと技術の蓄積をもたらしました。1853年にペリーが浦賀に来航し、欧米列強の脅威から尊王攘夷運動が高まると、加賀藩も1862年に七尾軍艦所を設立し、沿岸の各台場に数門の大砲を設置した。能登の鋳物技術の系譜は、この軍艦(修造)と大砲の製造者にまで遡ることができる。古くから塩田の生産で栄え、後に加賀藩の庇護を受けた鋳物師たちは、明治維新という激動の時代にさらなる苦難を強いられた。その中で培われた創意工夫と技術革新は、現在に続く製造業の礎となった。
加賀羽二重は、京都から力織機が導入された江戸時代初期から全国的に知られていたが、明治中期になると、ハンカチなどに適した薄手の羽二重が輸出品として注目されるようになりました。生産拡大のため、1870年代後半には桐生(群馬県)から羽二重織りの技術が導入され生産は拡大していきました。興味深いのは、1886年(明治19年)、武士の実業家・河井辰太郎が著書『金沢論』の中で、「金沢は、製糸織物を以もって産業と定むべき」 と述べていることです。 絹織物の生産性を高めるため、津田米次郎は日本初の力織機の開発に力を注ぎ、新興の織元である水藤勇太郎は津田式力織機を導入して機械工場を稼働させました。 金沢の羽二重織は、もともと福井の羽二重織の成功に追随する形で始まったが、織物業を追求するだけでなく、力織機を生み出し、機械工業の分野に進路を定めたことは、福井県とは異なる特徴的な点であり、現在の石川県の機械工業発展の基礎となっている。
忘れてならないのは、絹の力織機が県内各地や全国の繊維産地の需要に応え、さまざまな工夫を経て、多種多様な技術が蓄積されていったことである。実際、力織機の生産は津田米次郎に始まり、本多式、松川式、田村式、杉本式など次々と新しい力織機が発明され、そのたびに性能と技術が向上し、明治から大正にかけて20種類以上の力織機が世に送り出された。やがて金沢の織機は全国で使われるようになり、海を渡って朝鮮半島にまで輸出されるようになりました。